Encrypted Virus Attack: What are They and How to Prevent Them?
Last Updated : 27 Jun, 2024
 1.68L
1.68L

Introduction
“Convenience meets consequence” – is exactly what defines our growing reliance on digital systems, unlocking the fear of intrusion, data theft, and even identity theft.
While digital devices assure transformative convenience, their widespread adoption has also triggered a significant rise in cyber breaches. Among the various cyber breaches frequently reported in the news, encrypted virus is the most feared by organisations. Also known as ransomware, the virus accounts for an alarming surge of 55.5% of cyber incidents worldwide. The latest victim of ransomware attack is Indonesia’s national data center which was subjected to pay a whopping $8 million ransom.
So, what is ransomware and how does it work? This blog sheds light into the major aspects of encrypted virus aka ransomware.
Overview of encrypted virus
What if your PC starts not responding to your command one fine day? Or you discover that are you suddenly unable to access stored files and information on your device? This can be a probable ransomware attack or encrypted virus that can cost the victim a fortune to recover.
An encrypted virus is a cunningly designed malware that can evade detection by antivirus programs. It works by encoding its payload with encryption, making it difficult for security systems to recognise and analyse.
On infecting a system, it encrypts itself to execute its harmful actions, such as stealing data or corrupting files. The encryption methods used can vary, often changing its nature with each infection to avoid detection. As of 2024, some of the most common types of ransomware attacks are CryptoLocker, WannaCry, Bad Rabbit, Petya, etc.
Preventing encrypted viruses is crucial as they pose a significant threat to data security, especially for organisations that thrive on billion-dollar data. To combat these advanced breaches, organisations must adopt robust cybersecurity measures and constant vigilance to prevent system infection and data theft.
How does an encrypted virus work?
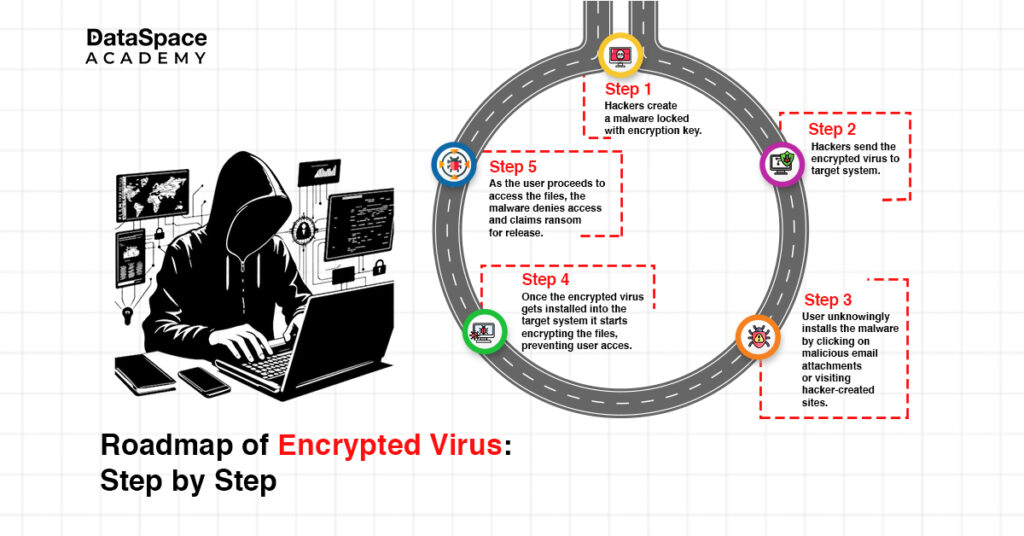
Encrypted viruses can land on your system through various means such as email attachments or unverified downloads. You can also end up installing it in your system by unknowingly accessing malicious websites. At the core of the encrypted virus is its strong encryption algorithm that can only be decrypted by the attacker holding a unique key.
To help you understand this complex encryption, we decrypt the process in the simplest language below:
The process begins with the creation of encryption keys that the threat actors create offline. The encrypted key is inserted into the malware before launching an attack. Once launched, this malicious code starts encrypting the files and resources in your system, holding them to claim ransom.
AES- RSA encryption method
The use of AES- RSA encryption method has made this encryption code harder to crack, therefore making it the hacker’s favorite attack mode. The most alarming part is, that the virus starts encrypting files without users’ permission and acknowledgment.
Can you Decrypt?
Now, the next concern is- is it possible to decrypt the ransomware virus? Yes indeed, but in most cases the victim has to depend on the miscreants to restore access. This is possible once the ransom is paid. The encrypted virus will then launch a tutorial for the victim to recover the decryption key. Next, the victim will be then directed to a page to download the necessary decoder.
However, if there is no demand for decryption, there is a possibility of the infection taking charge of the afflicted systems.
Distribution of the virus
As viruses and ransomware are increasingly threatening our digital security, we tend to neglect the ways they gain access to our systems. Shockingly, we often fail to recognise that we are the ones allowing them in.
How?
Blame it on our poor digital literacy and greed in most cases. To inject your system with ransomware, cybercriminals implement the most common tactics like harmful redirects, spam emails/ campaigns, and software/app installation. Lack of awareness about basic cyber hygiene can make users an easy target.
However, in certain cases, miscreants specifically target a computer or network system, resulting in DDoS (distributed denial of service), and identification threats.
Nature of ransomware attacks:
- Erase files regardless of whether the ransom is paid or not
- Compel victims to pay for committing a crime for accessing obscene content or engaging in illegal activities. This threat type usually comes masked as a property from law enforcement agencies

Tips to Stay Safe from Ransomware Attacks:
Folow our recommended expert safety tips to safeguard both your digital identity and wallet from encrypted viruses.
- Do not click on links of spam mail from unknown sources or with a suspicious domain extension
- Keep your device and software updated with the latest security patches and OS versions
- Install anti-spyware software in your devices
- Turn ‘firewall’ ON
- Use stronger authentication login methods
- Don’t click out of flick
- Shop safely and share data mindfully
- Parental guidance is recommended for children accessing the internet
Conclusion
Encrypted viruses pose an evolving threat in the cybersecurity landscape, combining sophisticated encryption techniques to evade detection and wreak havoc. As these threats advance, the importance of staying informed and vigilant are crucial.
Equally critical is fostering awareness among users and organisations about safe digital practices. By staying educated about potential risks and implementing proactive measures, we can mitigate the impact of encrypted viruses and protect our digital assets – therefore ensuring a safer cyber future.
Future cybersecurity efforts must focus on developing advanced detection methods and robust encryption-breaking tools. Rising cyber threats has led to an increasing demand for cybersecurity experts who can launch a mighty fight agaisnt these menacing attacks. You can enroll for our industry-leading cyber security certifications to build a successful career in digital security.
 1.68L
1.68L