Top 50+ Networking Terms To Know
Last Updated : 26 Feb, 2024
 1.38L
1.38L

Introduction
Network administrators are the backbone of the contemporary IT-driven world. With more and more organisations shifting their operations on-cloud, demand for skilled network professionals is at ATH (All-Time-High). They need skilled network techies who can manage their operations and fix the snags within the network to ensure a safe IT environment. A network administrator in India can earn up to ₹10 to 12 LPA annually. In other words, a career in networking is your key to making it big in life. And, the first step to delve into the networking world is to begin with a clear know-how of computer networking terminology. The blog here sheds light on some of the basic networking terms that every aspiring network professional should be acquainted with.
We will walk you through the top 50 networking terms that will demystify the complexities of computer networks. From the basics of LAN and WAN to the intricacies of protocols like TCP/IP and DNS, we’ve got you covered.
Let’s dive in and unlock the secrets of computer networking terms!

Major Networking Terms
Let’s get started with the basic networking terms.
- Bandwidth: It refers to the maximum volume of data which could be transmitted over a computer network, in a specific time period.
- Bridge: A networking device that connects two or more network segments or LANs.
- Broadcast: A type of network communication where data is sent to all devices on the network.
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol): This network protocol automatically assigns IP addresses to connected devices across a network.
- DNS (Domain Name System): This system is your translator for translating human-legible domain names right into the IP addresses.
- Firewall: A security device or software that filters network traffic based on predefined rules.
- Gateway: A network node that connects two different networks, facilitating communication between them.
- Hub: A simple network device that connects multiple devices together in a star topology.
- IP Address: It can be defined as a distinct numerical identifier which is assigned individually to every device within one particular network. This is one of the most crucial terms to remember when you are aspiring for a career in computer networking.
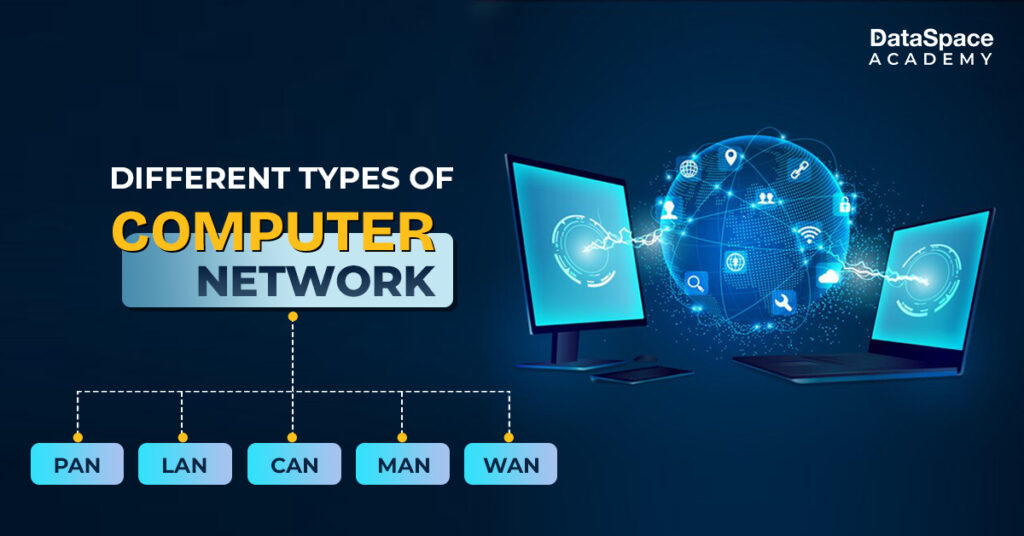
- LAN (Local Area Network): This refers to the network that is designed connect several devices installed within one particular geographical area.
- MAC Address (Media Access Control Address): A unique hardware address assigned to each network interface card (NIC).
- NAT (Network Address Translation): A technique that allows multiple devices to share a single public IP address.
- OSI Model (Open Systems Interconnection Model): A conceptual framework for understanding network communication.
- Packet: You can refer it as a data unit which is transmitted right over a computer network.
- Protocol: A set of rules that govern how data is transmitted and received in a network.
- QoS (Quality of Service): Techniques used to prioritize certain types of network traffic to ensure better performance.
- Router: This networking device is entrusted with the responsibility to forward data packets in between networks.
- SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol): Technically speaking, it’s a protocol assigned for managing as well as monitoring network devices.
- SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security): Protocols used to provide secure data encryption in network communications.
- Subnet: A smaller division of an IP network, created to improve network performance and manageability.
- Switch: A networking device that connects multiple devices together in a star or mesh topology.
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): A reliable and connection-oriented protocol used for data transmission.
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol): A connectionless and less reliable protocol used for data transmission.
- VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network): A logical partitioning of a physical LAN into smaller virtual networks.
- VPN (Virtual Private Network): A secure and encrypted private network connection over a public network.
- WAN (Wide Area Network): A network that spans a large geographical area, connecting multiple LANs.
- CAN (Campus Area Network): As the name says, this computer network is used to connect several buildings within one large property- such as a university campus.
- MAN (Metropolitan Area Network): It does the same thing that WAN does, i.e. connecting several LANs within a huge geographical area. However, MAN’s scope of coverage is smaller than that of WAN.
- PAN (Personal Area Network): This computer networking terminology refers to the computer network that interconnects multiple electronic devices installed in a single workspace.
- WAP (Wireless Access Point): This refers to a device that enables easy connection of wireless devices with wired network.
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy): An older and less secure wireless network encryption standard.
- WPA/WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access): More secure wireless network encryption standards.
- BGP (Border Gateway Protocol): A routing protocol used between different autonomous systems on the internet.
- DHCP Server: A network server that provides IP address allocation using DHCP.
- DNS Server: A server that stores DNS records and provides IP address resolution for domain names.
- Domain: A group of devices under the same administrative control within a network.
- Ethernet: A standard for wired network communication.
- Gateway Router: A router that serves as an entry and exit point for traffic between networks.
- Half-Duplex: A communication mode where data can be transmitted or received, but not simultaneously.
- ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol): A network protocol used for error reporting and diagnostics.
- Intranet: This refers to the private network that limits access solely to authorised personnel within a particular organization.
- ISP (Internet Service Provider): This is a company that extends complete internet access to customers.
- Latency: The time delay between sending and receiving data in a network.
- Load Balancing: The distribution of network traffic across multiple paths or devices to optimise performance.
- Modem: A device that modulates and demodulates analog signals for digital data transmission.
- Multicast: A type of network communication where data is sent to a specific group of devices.
- NAT Firewall: A firewall that incorporates Network Address Translation functionality.
- Packet Loss: The percentage of data packets that are lost during transmission.
- Port Forwarding: The process of redirecting network traffic from one port to another.
- Proxy Server: A server that acts as an intermediary between clients and other servers.
- RIP (Routing Information Protocol): A distance-vector routing protocol used in some networks.
- Subnet Mask: A numeric value used to determine the network and host portions of an IP address.
- VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol): Technology for making voice calls over IP networks.
Conclusion
By understanding the fundamentals of networking and network protocols, you can build a strong foundation on network infrastructure. To help you better grasp the concept of networking and system administration, DataSpace Academy has introduced numerous courses like ccna course in kolkata. However, the course is available for networking students globally and is designed to help you crack the CCNA exam. Additionally, the leading academy also extends an industry-leading Certification In AWS Solution Architect Training.
The reputed networking training institute focuses on the most essential tools and techniques like CISCO Packer Tracer and Elastic Block Storage that can help in building a career in this domain. Apart from classroom training, you get a chance to work on hands-on projects that enhance your skills further. At the end of the course, DataSpace Academy’s placement assistance support helps you find relevant jobs that align with your skills.
 1.38L
1.38L